What does CNS and PNS stand for? Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
What are the parts of the CNS? Brain and spinal cord
Describe something that you do on a regular basis that your PNS controls. Feel/touch
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system and what does each control? Sympathetic and parasympathetic. Sympathetic controls actions or movement and parasympathetic controls your emotions.
What are the three main types of neurons? What is the function of each? Sensory neuron – which control your sense of feeling(touch), motor neuron – controls your movement/actions, and inter neuron – sends messages to the CNS.
What is the function of the axon of a nerve cell? The dendrite? The axon conducts a nerve impulse away from a neuron cell body. The dendrite transmits impulses towards a neuron cell body.
What is a synapse? This is the junction between the axon of one neuron and dendrite or cell of another neuron.
Sketch a neuron and label the axon and the dendrite.
Thursday, September 27, 2007
Wednesday, September 26, 2007
Skeletal Muscle Worksheet
What percent of the body is smooth muscle? Striated muscle? 5% to 10% is smooth muscle and 40% is striated muscle
Name 3 types of muscle proteins. What is the function of each? Stroma – an inert structural element, or skeleton, to hold the rest of the structures together. Cellular – these proteins are not specifically characteristic of muscle since they are also found in other metabolically active cells. Contractile – two types: myosin and actin that are essential for contraction.
What is a myofibril? A muscle fiber
Sketch a picture of a sarcomere. Label the I-band, the A-band, the Z-line and the H-zone.
Name the two filaments that make up a sarcomere. Myosin and Actin
Draw a sarcomere at rest, stretched out and contracted.
What is the sliding filament theory? This theory is the state that the sarcomere is in. When the thick and thin filaments move across each other.
Muscle relaxation ensues upon the removal of what? Calcium ions
Name 3 types of muscle proteins. What is the function of each? Stroma – an inert structural element, or skeleton, to hold the rest of the structures together. Cellular – these proteins are not specifically characteristic of muscle since they are also found in other metabolically active cells. Contractile – two types: myosin and actin that are essential for contraction.
What is a myofibril? A muscle fiber
Sketch a picture of a sarcomere. Label the I-band, the A-band, the Z-line and the H-zone.
Name the two filaments that make up a sarcomere. Myosin and Actin
Draw a sarcomere at rest, stretched out and contracted.
What is the sliding filament theory? This theory is the state that the sarcomere is in. When the thick and thin filaments move across each other.
Muscle relaxation ensues upon the removal of what? Calcium ions
Monday, September 24, 2007
Tuesday, September 18, 2007
Skeleton Anatomy Worksheet
Describe the 4 functions of bones. Supports the body, protects innards, production of blood cells, and store various minerals and salts.
How many bones are there in the human body? 206
What are the two divisions of the skeletal system? Name 5 specific bones in each division. Axial skeleton(sternum, clavicle, vertebral column, rib cage, and pelvis) and appendicular skeleton(humerus, radius, ulna, femur and patella).
What bone makes up the upper arm? humerus
What bone makes up the face? skull
Name two bones that protect vital internal organs. Rib cage and skull
What bone in the forearm is always on thumb side? radius
What bone is movable for back muscles to attach to? scapula
What bone is also known as the shin bone? tibia
Sketch a human skeleton and label the following bones: skull, clavicle, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, patella, femur, tibia, fibula, pelvis, vertebral column, scapula and rib cage.
How many bones are there in the human body? 206
What are the two divisions of the skeletal system? Name 5 specific bones in each division. Axial skeleton(sternum, clavicle, vertebral column, rib cage, and pelvis) and appendicular skeleton(humerus, radius, ulna, femur and patella).
What bone makes up the upper arm? humerus
What bone makes up the face? skull
Name two bones that protect vital internal organs. Rib cage and skull
What bone in the forearm is always on thumb side? radius
What bone is movable for back muscles to attach to? scapula
What bone is also known as the shin bone? tibia
Sketch a human skeleton and label the following bones: skull, clavicle, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, patella, femur, tibia, fibula, pelvis, vertebral column, scapula and rib cage.
Joint Anatomy Worksheet
Why is there little to no movement in a fibrous joint? Because the bones making up the joint are united with strong fibrous tissue.
What is an example of a fibrous joint? The bones that hold your skull together.
Describe a cartilaginous joint and give an example. When two bones are united by intervening fibrocatilage.(vertebral column)
What type of joint essentially allows free movement? Synovial joints
What lubricates a joint cavity? cartilage
For the following joint types please list the name of the joint type, the type of movement of the joint, the shape of the joint and an example.
Plane joint – gliding or slipping, slightly curved surfaces, the wrist.
Hinge joint – rotation, irregular cylinder and/or concave groove, elbow joint.
Condylar joint – rotation and more, condyles, knee joint.
Ball and Socket joint – variety of directions, spherical articulation and cup-shaped cavity, shoulder joint.
Ellipsoidal joint – same as ball-in-socket except oval circumference, moves in various directions, wrist joint
Pivot joint – rotates(pivot), bony peg and concave notch, radius and ulna.
Saddle joint – varions directions, resembles two western saddles, bottom of the thumb.
What is an example of a fibrous joint? The bones that hold your skull together.
Describe a cartilaginous joint and give an example. When two bones are united by intervening fibrocatilage.(vertebral column)
What type of joint essentially allows free movement? Synovial joints
What lubricates a joint cavity? cartilage
For the following joint types please list the name of the joint type, the type of movement of the joint, the shape of the joint and an example.
Plane joint – gliding or slipping, slightly curved surfaces, the wrist.
Hinge joint – rotation, irregular cylinder and/or concave groove, elbow joint.
Condylar joint – rotation and more, condyles, knee joint.
Ball and Socket joint – variety of directions, spherical articulation and cup-shaped cavity, shoulder joint.
Ellipsoidal joint – same as ball-in-socket except oval circumference, moves in various directions, wrist joint
Pivot joint – rotates(pivot), bony peg and concave notch, radius and ulna.
Saddle joint – varions directions, resembles two western saddles, bottom of the thumb.
Thursday, September 13, 2007
Tuesday, September 4, 2007
Study Questions
Distinguish between the study of anatomy and the study of physiology.
Anatomy is the study of the structure of body parts and Physiology is the study of the functions of the body parts.
Give an example that shows the relationship between the structure and function of body parts. The stomach is a J-shaped, pouch-like organ, and it also stores food.
List the levels of organization within the human body in reference to a specific organ. Heart – circulatory system – muscle cells.
Distinguish between a midsagittal cut, a transverse cut, and a frontal cut. A midsagittal cut makes a line of symmetry, a transverse cut, cuts body into top and bottom halves, and frontal cut, cuts body into front and back.
Distinguish between dorsal and ventral body cavities, and name two smaller cavities that occur within each. Dorsal cavity – is the cavity in the back; contains cranial cavity and spinal cavity. Ventral cavity – the cavity in the front; contains thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.
Define homeostasis, and explain its importance. Homeostasis means that the human body’s internal environment remains relatively constant. It is important because it is really what helps us stay and keeps us alive.
Objective Questions
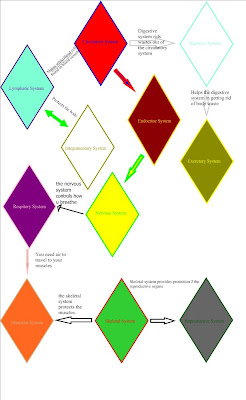
Thyroid gland – g (endocrine system)
lungs – c (respiratory system)
heart – d (circulatory system)
ovaries – e (reproductive system)
brain – f (nervous system)
stomach – a (digestive system
kidneys – b (urinary system)
A(n) cell is composed of several types of tissues and performs a particular function.
The imaginary plane that passes through the midline of the body is called the transverse plane.
All the organ systems of the body together function to maintain homeostasis, a relative constancy of the internal environment.
Medical Terminology Reinforcement
Gastrectomy means excision of the stomach.
Macrocephalus means large head.
Transthorasic means across the chest.
Bilateral means two or both sides
Dorsalgia means pain in the back
Endocrinology is the study of the endocrine system.
Study Questions
Describe the structure and function of endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum forms a membranous system of tubular canals and branches throughout the cytoplasm
Describe the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus. Mention vesicles and lysosomes in your description.
Describe the structure of mitochondria mention the energy molecule ATP in yoyr description. It produces ATP molecules, burns glucose to produce ATP.
Contrast passive transport (diffusion, osmosis, and filtration) with active transport of molecules across the plasma membrane. Active is movement that requires energy, passive just happens on its own.
Objective Questions:
Part 1
Packaging and secretion – golgi apparatus
Cell division - centriole
Powerhouse of the cell – mitochondria
Protein synthesis – Rough ER
Control center of the cell – Nucleus
Objective Questions pg. 61
What is a tissue – a group of similar cells that perform a specialized function.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue, and give location for each – protects the body from drying out, injury, and bacterial invasion.
What are the functions of connective tissue? Name the different kinds of connective tissue and give a location for each – binds structures together, provides support and protection, fills spaces produce blood cells and stores fat.
What types of cells does nervous tissue contain? Which organs in the body are made up of nervous tissue? Found in the brain and spinal cord and contains conducting cells called neutrons.
Anatomy is the study of the structure of body parts and Physiology is the study of the functions of the body parts.
Give an example that shows the relationship between the structure and function of body parts. The stomach is a J-shaped, pouch-like organ, and it also stores food.
List the levels of organization within the human body in reference to a specific organ. Heart – circulatory system – muscle cells.
Distinguish between a midsagittal cut, a transverse cut, and a frontal cut. A midsagittal cut makes a line of symmetry, a transverse cut, cuts body into top and bottom halves, and frontal cut, cuts body into front and back.
Distinguish between dorsal and ventral body cavities, and name two smaller cavities that occur within each. Dorsal cavity – is the cavity in the back; contains cranial cavity and spinal cavity. Ventral cavity – the cavity in the front; contains thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.
Define homeostasis, and explain its importance. Homeostasis means that the human body’s internal environment remains relatively constant. It is important because it is really what helps us stay and keeps us alive.
Objective Questions
Thyroid gland – g (endocrine system)
lungs – c (respiratory system)
heart – d (circulatory system)
ovaries – e (reproductive system)
brain – f (nervous system)
stomach – a (digestive system
kidneys – b (urinary system)
A(n) cell is composed of several types of tissues and performs a particular function.
The imaginary plane that passes through the midline of the body is called the transverse plane.
All the organ systems of the body together function to maintain homeostasis, a relative constancy of the internal environment.
Medical Terminology Reinforcement
Gastrectomy means excision of the stomach.
Macrocephalus means large head.
Transthorasic means across the chest.
Bilateral means two or both sides
Dorsalgia means pain in the back
Endocrinology is the study of the endocrine system.
Study Questions
Describe the structure and function of endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum forms a membranous system of tubular canals and branches throughout the cytoplasm
Describe the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus. Mention vesicles and lysosomes in your description.
Describe the structure of mitochondria mention the energy molecule ATP in yoyr description. It produces ATP molecules, burns glucose to produce ATP.
Contrast passive transport (diffusion, osmosis, and filtration) with active transport of molecules across the plasma membrane. Active is movement that requires energy, passive just happens on its own.
Objective Questions:
Part 1
Packaging and secretion – golgi apparatus
Cell division - centriole
Powerhouse of the cell – mitochondria
Protein synthesis – Rough ER
Control center of the cell – Nucleus
Objective Questions pg. 61
What is a tissue – a group of similar cells that perform a specialized function.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue, and give location for each – protects the body from drying out, injury, and bacterial invasion.
What are the functions of connective tissue? Name the different kinds of connective tissue and give a location for each – binds structures together, provides support and protection, fills spaces produce blood cells and stores fat.
What types of cells does nervous tissue contain? Which organs in the body are made up of nervous tissue? Found in the brain and spinal cord and contains conducting cells called neutrons.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)